Introduction¶
LightNet is a light-weight neural network inference optimizer for different software/hardware backends.
The deep learning algorithms for various application scenarios are becoming more and more mature. However, highly real-time algorithms in terminal devices such as Edge Computing Devices or Autonomous Agents (such as unmanned vehicles and drones) often require heterogeneous computing systems which are low-power and highly real-time. Such heterogeneous computing systems generally need to be developed with specific hardware-related languages (such as CUDA, OpenCL, Verilog, C/C++ etc.), which have the disadvantages of low development efficiency and long iteration period.
In order to overcome those shortcomings, LightNet refers to traditional compiler optimization technologies, designs and develops a neural network optimizer for heterogeneous platforms, which can accept neural network models from various popular deep learning frameworks, optimize them according to the user's choice of backend platforms, and save the optimized models which can be directly run by LightNet.
LightNet for now mainly focuses on the high-level optimization of a NN model, which can be completed with substitutions of the operators in a computing graph (data flow graph). Those optimizations are processed by the peephole optimizers and graph substituters of the corresponding backend, according to the optimization capabilities provided by the backend platforms (architecture). After the high-level optimizations, LightNet will plan the relative memory address used by each tensor, which can be converted to real memory address at runtime, at the same time keep the total memory usage as low as possible.
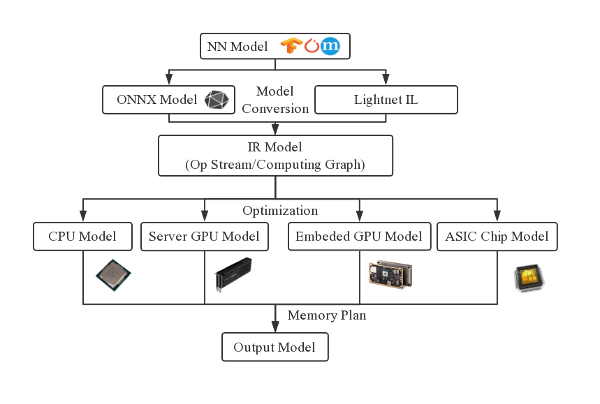
LightNet essentially is an end-to-end NN optimizer framework that can be easily extended to support different model formats and backend computing platforms. However there are 3 diversification problems when designing such an optimizer which leads to enormous coding efforts:
- diversification of model formats, such as Tensorflow's checkpoint, Pytorch's pt.
- diversification of operators, operators are highly diverse and new operators are emerging.
- diversification of operator optimization capabilities of different backend platforms.
LightNet provides 3 methods to solve those problems respectively:
- a unified model format and conversion tools for various frameworks
- an operator description language and code generation tools
- an optimizer description language and code generation tools
Combined with the above methods, LightNet can be easily extended to support different model formats, all kinds of operators, and various backends with different optimization capabilities, to realize the rapid construction and automatic optimization of NN models.
LightNet's core architecture is developed with C, which has the advantages of light weight, high efficieny and unified binary interface, which can be easiy combined with other languages and deployed in various hardware platforms.